Scientists and experts can help prepare for record shattering heatwaves
by ISR Staff

Last year, the world shattered a record we never should have hit: our warmest year ever. In response, UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres remarked that we are in an “era of global boiling,” as he called for swift action on human-induced climate change. So far in 2024, global temperatures have continued to break monthly records as prolonged heatwaves are impacting millions of people worldwide, from India to Mexico.
Researchers from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) also found that for the average person on Earth, there would be 26 additional days of extreme heat this year, compared to if climate change was not happening. In certain regions of the world, that number reaches as high as an extra 120 days.
Urban residents, who represent more than 55% of the world’s population, are particularly at risk from these warmer temperatures due to urban heat islands (UHIs), which occur when a city’s infrastructure, like roads, parking lots, and rooftops, absorb and remit heat more than natural landscapes like forests. In effect, UHI makes urban environments hotter than rural locations.
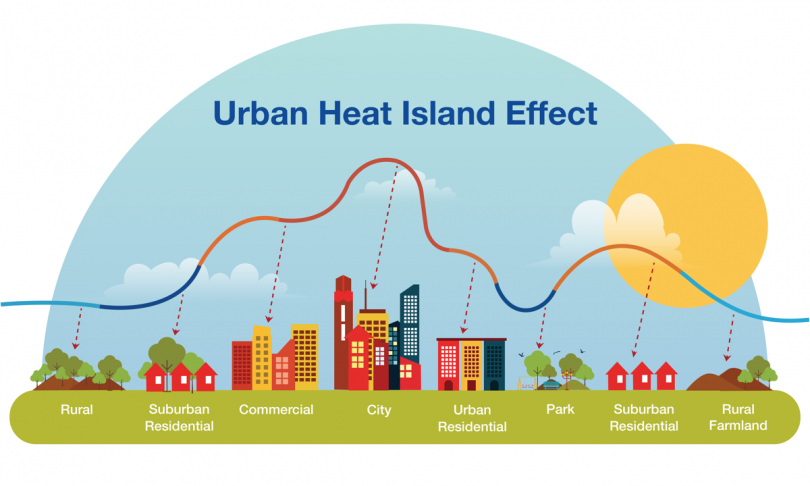
The greenhouse gas emissions that humans have already emitted into the atmosphere means that extreme heat is not going away anytime soon, even if we rapidly reach climate targets and zero emissions. That’s why, as a network of scientists and experts concerned about crisis, we can be thinking of new ways to collaborate to inform, prepare, and reduce harm to humans and ecological systems during extreme heat waves.
The Limits of Heat on the Human Body
Climate change is already affecting human health. There are risks to human bodies from extreme heat, particularly for residents in cities, and within communities that are more vulnerable to its adverse impacts. Extreme heat is more dangerous for children, older adults, and outdoor workers – particularly those who do not have labor protections to keep them safe.
Of particular concern to human health is when heat and humidity remain high in combination, especially at night. It becomes difficult for the body to rest, relax, and stabilize – and that can put the body under significant stress.
More and more experts are calling for decisionmakers to gauge upcoming risks to the public by using a wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) reading versus temperature alone. WBGT is measured through temperature, humidity, wind speed, sun angle, and cloud cover. Tropical and coastline cities, for example, are already reaching critical “wet bulb” temperatures, where the human body cannot cool down through its normal sweating process because sweat is not able to evaporate in high humidity. Dry heat is cooler for the body, for this reason.
Experts define 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius) as the upper limit of WGBT for young and healthy people. During India’s recent heatwave, the WGBT reached at least 100 degrees (37.8 degrees Celsius), making the chances of heat exhaustion, stroke, and even death much higher for vulnerable populations.

Cities in China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, India, the Arabian Peninsula, and the African Sahel are among the highest risk zones for dangerous levels of WGBT. Jacobabad, Pakistan is often called one of the hottest cities on earth and has experienced at least four extreme wet bulb events in recent years. Many cities lack the infrastructure or resources to deal with extreme heat, in some cases because in the past they did not need it.
Understanding the Toll of Extreme Heat
Unlike hurricanes, earthquakes, or tornadoes, heat disasters often go unseen by decisionmakers because the public health impacts often happen inside homes or go undiagnosed by health professionals as heat related.
In the US, the National Weather Service (NWS) cites that heat has been the deadliest form of extreme weather over the last decade. But many researchers believe current counts of heat illnesses death are vastly underestimated. In sub-Saharan Africa, for example, there is little to no accurate tracking of heat deaths. In 2022, a groundbreaking study found that approximately 70,000 people died in Europe due to the summer’s extreme heat. Europe is considered the fastest warming inhabited continent, and many countries lack common cooling mechanisms, such as air conditioning, in older buildings.
Additionally, the burden of heat is not often shared equally. In India after recent heatwaves, schools closed, agricultural supply chains were disrupted, and workers lost significant income. According to a recent report by the UN, the rising temperatures in India will reduce daily working hours by at least 5.8 percent by 2030. Loss of economic opportunity also acutely impacts women and girls.
What Experts Can Do to Respond and Save Lives
Just like with a hurricane or earthquake, the world’s most vulnerable cities need stronger preparation and mitigation measures to prevent and reduce severe health impacts. First and foremost, the rapid phaseout of fossil fuels is the most critical step to take to reduce harm.
Second, if scientists and health experts begin to treat extreme heat like other disasters, the public will be equipped with more tools to take the proper steps to help prepare for it. Early warning systems remain as one of the most effective ways to keep people safe, and countries with “limited early warning systems” are experiencing heat-related deaths at a rate eight times higher than countries that have comprehensive warning services.
In the US, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and NWS recently created a new scale that helps the public gauge health risks associated with extreme heat. HeatRisk considers several factors, such as time of year and length of heatwave, and models where elevated risks exist to help leaders better communicate on a clear scale of 1-4.
Scientists and health experts can also help the public better understand what to do once a warning about elevated risk occurs, including educating them on action steps like:
- Having a plan to acclimatize your body safely over time by gradually increasing activity outdoors,
- Staying in cool environments,
- Hydrating quickly and drinking electrolytes, when possible,
- Removing restrictive layers and wearing light layers,
- Taking a cold shower or bath when overheated,
- Avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and
- Reducing work in the sun.
Several major cities have also taken to hiring Chief Heat Officers who create Heat Action Plans, or roadmaps to help urban dwellers deal with heat. The World Economic Forum and Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center (Arsht-Rock) also created the Heat Action Platform, a free online resource that provides cities with tools to assess, plan, implement, and evaluate their heat plans.
Energy supply is also critical to preparations. Given the pressure on the energy grid in many countries, there has been an increase in rolling or prolonged blackouts due to high demand during heatwaves. Air conditioning therefore cannot be seen as the only stable solution to cool down. In just one month in Mexico, for example, over 32 states including Mexico City experienced blackouts. The loss of power can lead to life-threatening situations for people with disabilities, health conditions, and older adults. In the mid- to long-term, in order to reduce harm in many countries, there needs to be major updates to the power grid that are powered by renewable energy and stabilized through weatherizing of buildings for energy efficiency and planting more trees for shade and cool roofs.
If you want to learn more about how to collaborate with other researchers on scientific issues related to heatwaves, please join the International Science Reserve and RSVP for our upcoming heat webinar at the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)’s Science Summit this September.


